How do you charge an electric machine?

Charging station: The place or piece of equipment where you can plug in and charge an electric vehicle.
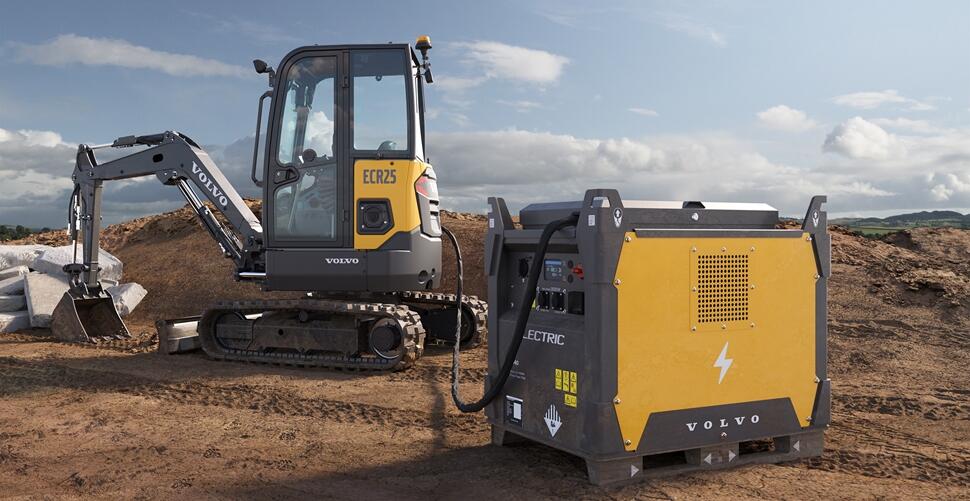
Power Unit (PU): An energy storage system designed to deliver reliable electric power for electric vehicles and other battery-powered tools. These come in a variety of sizes and are ideal where there is weak or low access to the grid.

Green or renewable charging: Charging using power generated from natural sources, such as wind, water, and sunlight rather than fossil fuels.
The Grid: An interconnected network that delivers electricity (AC current) from where it is produced, along power lines to the consumer.
Kilowatt (kW): The measure of electric power and energy output and is the same as 1,000 watts so in layman terms it tells you how much energy is being used or produced at a specific moment, EVs are rated by their kilowatt output so for example, a 100 kW machine uses energy much faster than a 10 kW machine. 1 kW is the equivalent of 1.341 horsepower (hp), the common unit of energy for measuring the power of internal combustion engines.
Kilowatt Hour (kWh): This is the amount of energy used or stored. It’s a useful measurement to determine the amount of power consumed over time and the battery capacity, as well as for comparing the runtime and charging time of electric vehicles.
Alternating Current (AC): Commonly known as the grid, AC is an electric current that frequently changes or alternates direction (hence the name!) and as a result, the voltage level also changes with the current. AC is widely used to supply electricity in homes and businesses, though the voltage and current levels vary between countries.
Direct Current (DC): DC is an electric current that flows in only one direction; hence the voltage remains constant. Batteries use DC, so devices like converters and inverters are needed in battery systems to switch between DC and the AC used in mains power.
Voltage (V): A measure of the difference in electrical energy between two parts of a circuit. The bigger the difference in energy, the bigger the voltage.
On-board charger: A device that converts AC voltage to DC voltage.
 Type 2 Connector: The IEC 62196 Type 2 connector features a seven-pin plug with one flat edge.
Type 2 Connector: The IEC 62196 Type 2 connector features a seven-pin plug with one flat edge.
DC Charger: A method for battery charging. The DC current is supplied directly to the batteries at the corresponding voltage through a DIN plug (48V machines) or Combined Charging System (CCS) 2 plug which combines a three-pin Type 2 AC connector with a two-pin DC connector.
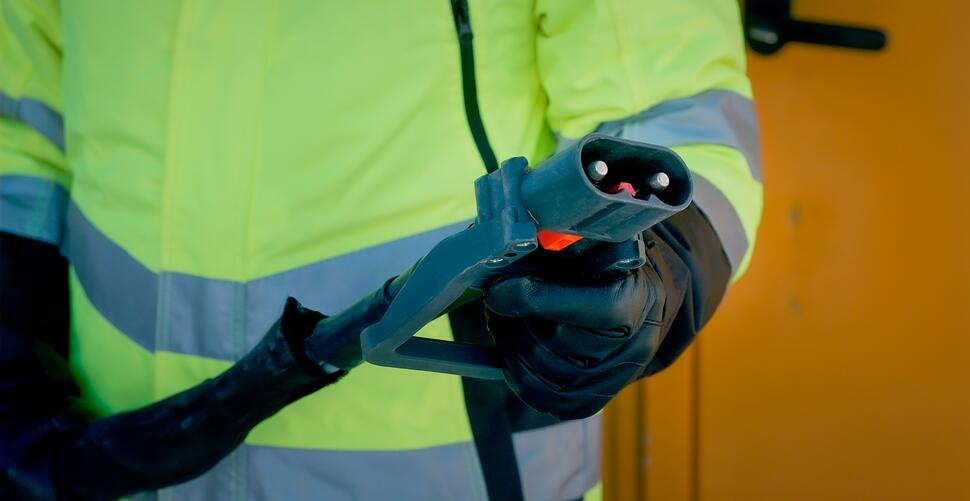
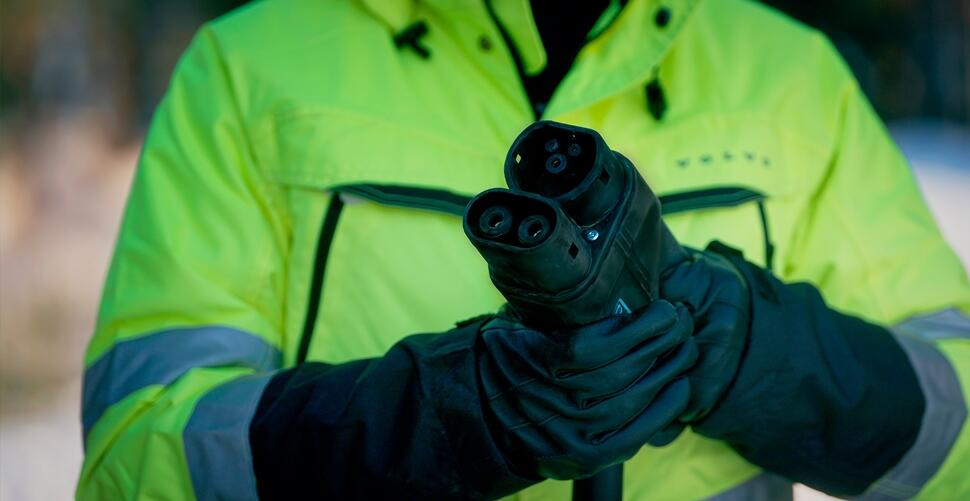


Outlets with Volvo Adapters for Charging Electric Equipment
The images below show you 1-phase and 3-phase outlets which are recommended for AC charging of BEVs or battery electric vehicles. There are variants of these in use across Europe.
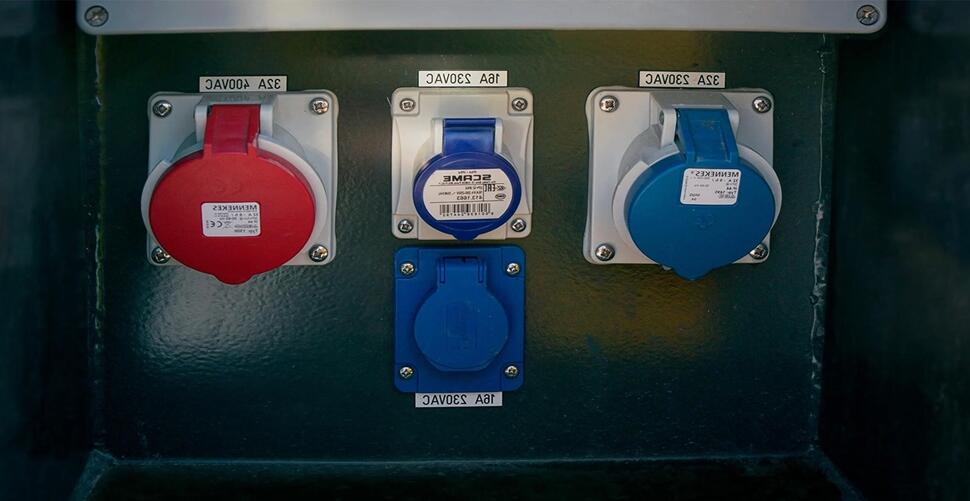

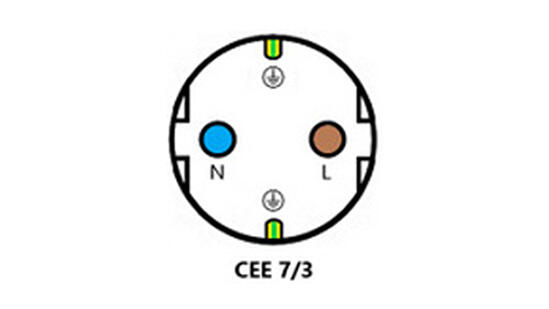 230 wall outlet 230 wall outlet |
 16A 1-phase outlet 16A 1-phase outlet |
 16A 3-phase outlet 16A 3-phase outlet |
 32A 3-phase outlet 32A 3-phase outlet |
AC charger: A method for charging EV batteries through an IEC 62196 Type 2 Connector.
State of Charge (SOC): An approximate measure of the amount of energy left in the battery. SOC is usually expressed as a percentage of the maximum charge.
Machine Run Time: The amount of time a machine can operate on a fully charged battery before it requires recharging.




